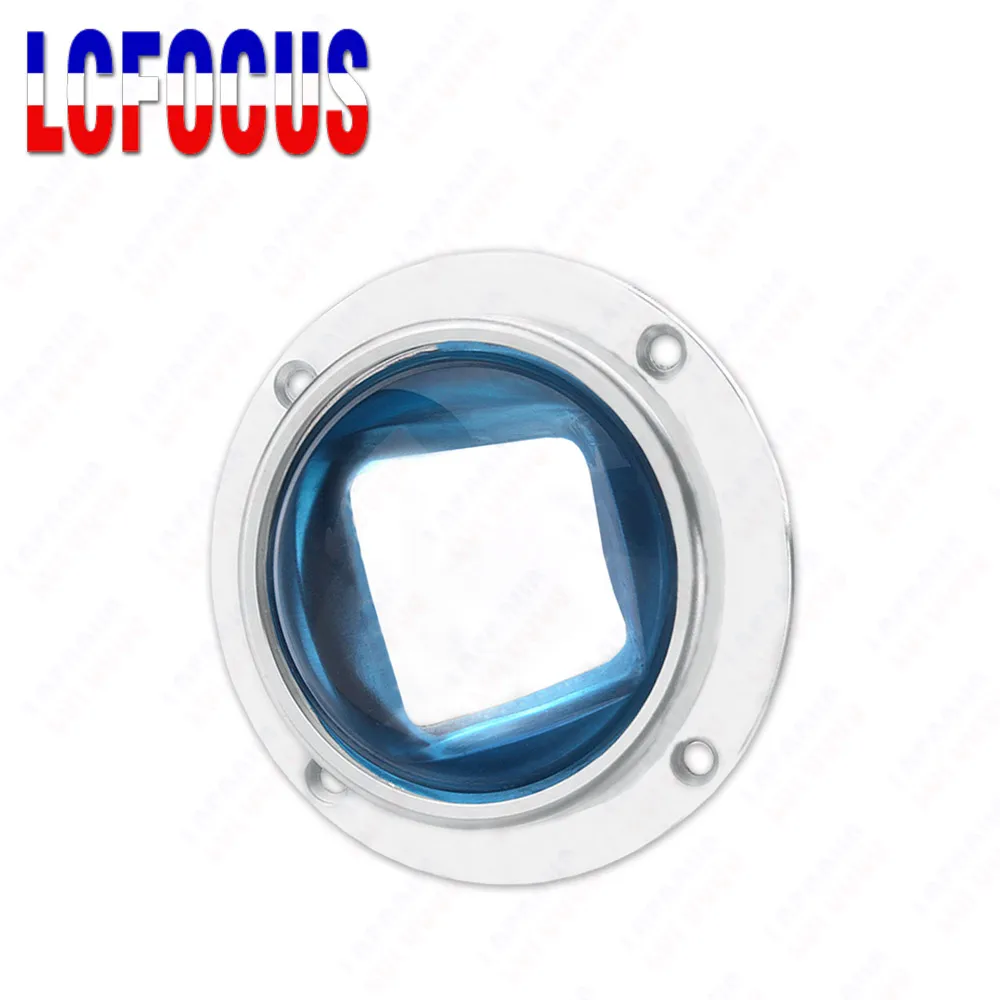
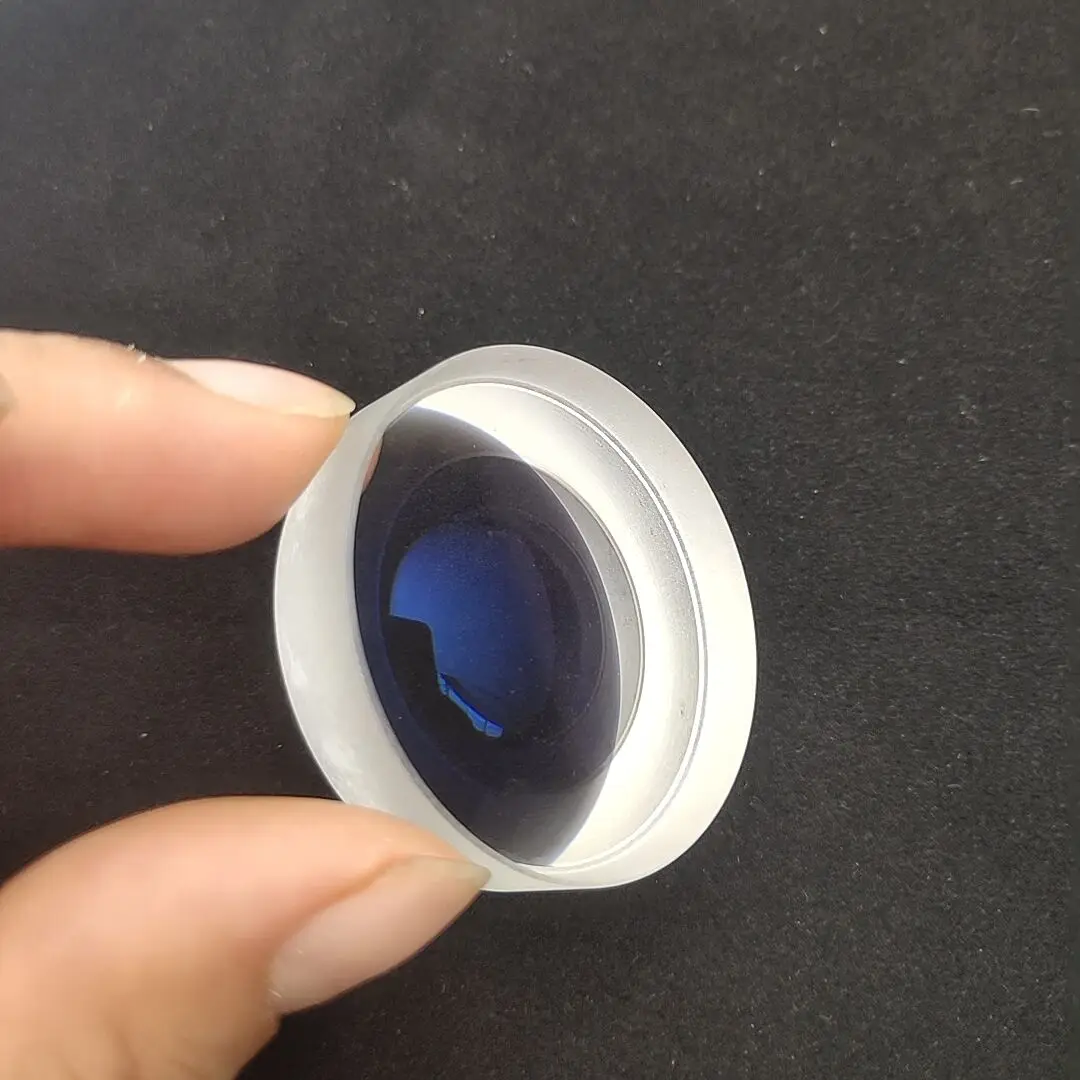
Новый продукт лазерный фокус Лен с GE Германий Материал Диаметр 12 мм FL 50.8
Сохраните в закладки:

История цены
*История изменения цены! Указанная стоимость возможно, уже изменилось. Проверить текущую цену - >
| Месяц | Минимальная цена | Макс. стоимость | Цена |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aug-17-2025 | 2821.84 руб. | 2877.64 руб. | 2849 руб. |
| Jul-17-2025 | 2288.46 руб. | 2334.20 руб. | 2311 руб. |
| Jun-17-2025 | 2776.63 руб. | 2832.50 руб. | 2804 руб. |
| May-17-2025 | 2754.87 руб. | 2809.15 руб. | 2781.5 руб. |
| Apr-17-2025 | 2199.20 руб. | 2243.44 руб. | 2221 руб. |
| Mar-17-2025 | 2710.51 руб. | 2764.23 руб. | 2737 руб. |
| Feb-17-2025 | 2687.32 руб. | 2741.42 руб. | 2714 руб. |
| Jan-17-2025 | 2665.30 руб. | 2718.59 руб. | 2691.5 руб. |
Новые товары
Алмазное Колесо для автомобильных эдгеров Nidek с V-образным пазом - купить по
Оптический экспериментальный диаметр 43 мм пользовательский вогнутый объектив
106 мм фокусное расстояние большого диаметра 600 900 двойное покрытие пленочные
Апертура для двойного преломления 80 мм стекло ахроматический объектив
Линза Френеля 520*520 мм F620 проекционная линза на солнечной батарее температура 500
Линза фокусировки CO2-лазера Wavelength Opex D12 18 19.05 мм 20 F76.2 50.8 63.5 для запчастей маркировочной машины RONAR-SMITH ZnSe.
Оптические стеклянные линзы планоконвексной формы для светодиодных фонарей, автомобильных фар, прожекторных светильников диаметром 12,5 мм, 15 мм, 16 мм, 18 мм, 30 мм, 35 мм, 38 мм и 40 мм.
высококачественная водонепроницаемая оптическая линза для светодиодных оконных ламп #NDIU-20, угол 3*60, размер 20X18мм, поверхность в виде полоски, изготовлена из ПММА.
Характеристики
Новый продукт лазерный фокус Лен с GE Германий Материал Диаметр 12 мм FL 50.8
Описание товара








Ge (Germanium) Materail Focus Len Diamater 12 mm, Thickness 3 mm
Focus Distance 50.8 mm (2 inch)
1>Diamater: 12 mm
2>Thickness: 3 mm
3>Materail: Germanium
4>Focus Distance: 50.8 mm
5> Suitable power: 30 to 50 W
Application: Spcecially used for the laser seal / stamp machine:

Germanium is a chemical element with symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors tin and silicon. Pure germanium is a semiconductor with an appearance similar to elemental silicon. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature.
Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the history of chemistry. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. Nearly two decades later, in 1886, Clemens Winkler found the new element along with silver and sulfur, in a rare mineral called argyrodite. Although the new element somewhat resembled arsenic and antimony in appearance, the combining ratios in compounds agreed with Mendeleev's predictions for a relative of silicon. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Today, germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though germanium is also recovered commercially from silver, lead, and copper ores.
Germanium "metal" (isolated germanium) is used as a semiconductor in transistors and various other electronic devices. Historically, the first decade of semiconductor electronics was based entirely on germanium. Today, the amount of germanium produced for semiconductor electronics is one fiftieth the amount of ultra-high purity silicon produced for the same. Presently, the major end uses are fibre-optic systems, infrared optics, solar cell applications, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Germanium compounds are also used for polymerization catalysts and have most recently found use in the production of nanowires. This element forms a large number of organometallic compounds, such as tetraethylgermane, useful in organometallic chemistry.
Germanium is not thought to be an essential element for any living organism. Some complex organic germanium compounds are being investigated as possible pharmaceuticals, though none have yet proven successful. Similar to silicon and aluminum, natural germanium compounds tend to be insoluble in water and thus have little oral toxicity. However, synthetic soluble germanium salts are nephrotoxic, and synthetic chemically reactive germanium compounds with halogens and hydrogen are irritants and toxins.
 Germanium has a wide range of special properties and has a wide range of important applications in such fields as semiconductors, aerospace monitoring and control, nuclear physics detection, optical fiber communications, infrared optics, solar cells, chemical catalysts, and biomedicine, and is an important strategic resource . In the electronics industry, in the alloy pretreatment, in the optical industry, it can also act as a catalyst.
Germanium has a wide range of special properties and has a wide range of important applications in such fields as semiconductors, aerospace monitoring and control, nuclear physics detection, optical fiber communications, infrared optics, solar cells, chemical catalysts, and biomedicine, and is an important strategic resource . In the electronics industry, in the alloy pretreatment, in the optical industry, it can also act as a catalyst.High-purity germanium is a semiconductor material. From the high purity of germanium oxide reduction, and then obtained by melting derived. Germanium single crystal doped with a trace of specific impurities can be used for a variety of transistors, rectifiers and other devices. Germanium compounds are used in the manufacture of fluorescent plates and various high refractive index glasses.
Ge single crystal can be used as transistor, is the first generation transistor material. Germanium materials for radiation detectors and thermoelectric materials. High-purity germanium single crystal with high refractive index, transparent to infrared light, visible light and ultraviolet light, can be used for infrared light through the germanium window, prism or lens. The early 20th century, germanium element used to treat anemia, after becoming the earliest application of semiconductor elements. Elemental germanium has a high refractive index, which is transparent only to infrared light and opaque to visible light and ultraviolet light. Therefore, military observers such as infrared night vision instruments use pure germanium to make lenses. Germanium and niobium compounds are superconducting materials. Germanium dioxide is a polymerization catalyst, germanium dioxide containing glass with higher refractive index and dispersion properties, for wide-angle cameras and microscope lenses, germanium trichloride or a new type of optical fiber material additives.

Remarks: we has large stock for this Germanium focus lens, and if you are the distributor with large quantity, please contact our online sales to talk for a bottom price, when you order reach 50 pieces at the first time.
Thank you~ Enjoy the laser work~













Трекер стоимости
Отзывы покупателей
Новые отзывы о товарах
Наконец то я приобрела очки, о которых давно мечтала. Спасибо продавцу. Цена радует меня. Качество очень хорошее. На лето... Читать отзыв полностью...
Всё идеально !Теперь у меня есть новые замечательные часы !))Только сегодня забрала их..очень эффектные и красиво смотрятся на руке ))вживую... Читать отзыв полностью...
Бобовые и овощные консервы торговой марки"Давыдовск� �й продукт" мы стали покупать частенько. Недавно увидели у них "Закуску новую" и взяли... Читать отзыв полностью...
Подала заявку на сайте на заказ постельного белья цвета шампанского. В этот же день начали исполнять мой индивидуальный заказ. Через... Читать отзыв полностью...
Скоро зимние праздники наступят и я нахожусь в поисках подарков моей жене... Думаю, что эта сумочка моей жене должна понравиться.... Читать отзыв полностью...
Нужна прошивка v8.3.2_20180925.105435_akw5 для магнитолы Asottu Z13SLT8060 Android 7.1... Читать отзыв полностью...










Красивое платье! Делала подарок маме на день рождения! Безупречно село, прям как будто на неё сшили. Всем очень понравилось, как... Читать отзыв полностью...